American Made, Iron Clad Protected - Discover the Industries Best Warranty.
Blog
Understanding Noise Regulations – When Is a Temporary Noise Barrier Legally Required?
When are Temporary Noise Barriers Legally Required?
Construction noise is more than an annoyance. It’s a safety concern that damages public health, community peace, and workers’ hearing. The constant noise of concrete saws, heavy machinery, and pile drivers has also become a legitimate concern. It leads to noise complaints from residents who live near construction sites. Schools, libraries, hospitals, and other public institutions are equally disturbed by such noise pollution.
State, federal, and local noise regulations play a crucial role in protecting worker safety and public health from excessive outdoor noise. If you are a construction site supervisor, developer, or contractor who wants to avoid heavy fines and maintain a reputable public image, it’s wise to understand specific regulations about noise mitigation. It’s also important to know when temporary construction noise barriers are legally required so you can easily stay compliant by following specific noise regulations.
In this guide, we’ll explore the noise regulations set by various authorities, explain why following a legal framework is essential to mitigate noise, and identify situations in which temporary construction noise barriers are required.
Construction Noise Regulations from Different Authorities
Construction professionals are often under pressure because they have to ensure that construction noise doesn’t exceed a specific limit. Therefore, it makes sense to know about the authorities that set noise regulations. Each one focuses on a different aspect but the common goal is to reduce harmful noise for community welfare.
Let’s explore these regulatory bodies and their noise regulations to reduce excessive construction noise.
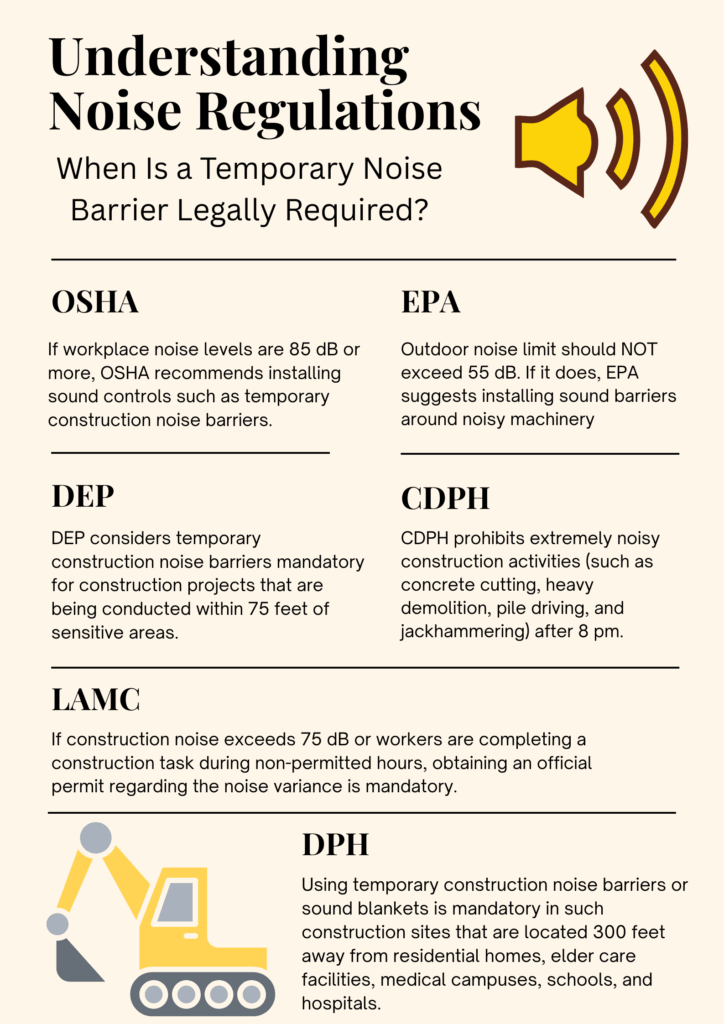
OSHA
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) provides on-site construction noise regulations for protecting workers’ hearing ability and overall health:
Maximum exposure limit: OSHA has set a noise limit of 85 dB for workers having an 8-hour work shift. It prohibits prolonged noise exposure beyond this limit and considers it hazardous.
When to take action: If workplace noise levels are 85 dB or exceed this standard limit, employers must introduce a hearing conservation program. However, failure to meet noise standards might lead to heavy fines (as much as $16,000 for a single violation).
Installing sound control: Incorporating administrative controls and equipment changes is the initial step towards reducing excessive noise and avoiding penalties. Installing sound-blocking enclosures is another way to achieve low-noise work environment. A temporary noise barrier is one such example of noise control options.
EPA
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has set regulations that help minimize the effects of excessive noise at the external level.
Noise limit: Outdoor noise limit shouldn’t go beyond 55 dB. The objective is to minimize noise pollution in a way that doesn’t disrupt residential communities’ peace. It’s especially applicable in construction sites that are located near schools, senior living places, or hospitals.
Installing sound control: EPA recommends that construction managers install sound barriers around noisy machinery (such as jackhammers, bulldozers, cranes, and industrial generators) to avoid sound transmission from the source.
Local ordinances
The most impactful and enforceable regulations are set by city governments. These organizations have the authority to suspend ongoing work and issue fines if employers fail to follow their noise control guidelines. They require noise mitigations according to local conditions.
Here are the noise regulations set by local authorities to limit construction noise:
DEP
The Noise Code designed by New York City Department of Environmental Protection (DEP) requires construction professionals to submit a noise mitigation plan before conducting any construction activities. Construction time slots are between 7 am and 6 pm on weekdays. However, constructing during weekends or off-hours requires you to apply for authorization.
Acoustic blankets or temporary construction noise barriers are mandatory for construction projects that are being conducted within 75 feet of residential communities, schools, or healthcare centers. Installing these noise barriers is also compulsory for construction activities that are being carried out within the time slots between 10 pm and 7 am. Failure to meet these guidelines can result in heavy fines (around $8000 for a single violation).
Chicago Municipal Code
Chicago City Council has stricter laws for controlling construction noise around community zones. Chicago Department of Public Health (CDPH) is the enforcement authority that prohibits extremely noisy construction activities (such as concrete cutting, heavy demolition, pile driving, and jackhammering) after 8 pm. However, it permits construction work from 8 am to 8 pm.
Construction sites near dense residential areas, schools, libraries, senior care houses, and hospitals must incorporate sound enclosures or temporary construction noise barriers in their noise mitigation initiative. The same is applicable if your construction project requires high-decibel machinery.
The Chicago authorities take aggressive action on non-compliance with noise regulations. Penalties can even be $10,000 for a single offense. Repeat violations might lead to project delays, cancellation of permits, and stop-work orders.
LA Municipal Code
The Los Angeles Municipal Code (LAMC) has set specific regulations for noise control. Construction projects in residential areas can be conducted from 7 am to 9 pm (on weekdays). On Saturdays, the permitted time slot is between 8 am and 6 pm. However, it doesn’t allow any construction activity on Sundays or public holidays.
The standard noise limit allowed in Los Angeles is 75 dB only. If your construction project exceeds this limit or your workers are completing a construction task during non-permitted hours, you must obtain an official permit regarding the noise variance. Besides, you should also install temporary noise barriers that can surround the construction site.
Police Code, San Francisco
San Francisco enforces its legislative framework according to its Police Code. The Department of Public Health (DPH) is the main authority that enforces this code. The city has confined its construction activities, i.e., from Monday to Friday (7 am – 8 pm). Inability to meet these timelines may result in fines up to $300.
San Francisco has strict regulations for construction sites that are located 300 feet away from residential homes, elder care facilities, medical campuses, schools, and hospitals. Using temporary construction noise barriers or sound blankets is mandatory in such construction sites. This rule is also applicable when a construction task operates during non-permitted hours or if construction equipment raises noise levels by five decibels.
When applying for a permit, constructors are required to prepare an official document explaining their noise control initiative. This document must include specific details, including projected noise sources, expected sound levels, and noise mitigation strategies.
Scenarios That Make Temporary Construction Noise Barriers a Legal Requirement
Using temporary construction noise barriers can be legally required in the following situations:
1. Noise exceeds the decibel limit
Construction equipment generating sound between 85 dB and 120 dB (or more) is a scenario that leads to non-compliance with noise regulations. In this case, you can use temporary noise barriers for reducing excessive construction noise.
2. Noise complaints
Annoyed nearby residents or even commercial business owners can file a complaint against you if the construction noise is too high. Consequently, local authorities may inspect your site. To avoid a work stoppage or a heavy fine, you can immediately install temporary noise barriers at your construction site.
3. Ongoing construction during off-hours
If your construction project requires early morning or nighttime work, you must keep noise decibels as low as fifty (or even lower). Temporary construction barriers will help keep construction noise within the range.
4. Construction near sensitive areas
Residential neighborhoods, hospitals, schools, and senior care centers are sensitive areas where construction noise isn’t tolerated. Local authorities inspect noise decibel levels of construction sites that are operating nearby such areas to ensure maximum peace and quiet. Temporary construction noise barriers work well in this situation.
The Takeaway
As urban development is rapidly increasing, it’s no surprise that construction is now an ongoing work in various regions. However, what matters is how construction managers responsibly plan and implement noise mitigation initiatives to protect workers as well as residents and neighborhoods from high-decibel noise.
Using temporary construction noise barriers near noisy construction equipment is a safe and effective way to maintain peace within the community. It also enables construction professionals to stay compliant with the noise regulations.
The key is to choose temporary construction noise barriers that offer a higher level of noise reduction. You should prefer composite and concrete ones made with MLV. Besides, you can check the sound levels of construction activities by making use of sound meters. This also ensures compliance while eliminating any chance of legal penalties.
Recent Posts
- The Silent Safety Hero: Why Fixed Draft Curtains Are Required in High-Rack Storage Facilities
- The Invisible Risk: How Contamination Happens Without Proper Warehouse Barriers
- Are Your Insulated Warehouse Curtains Compliant
- Understanding Noise Regulations – When Is a Temporary Noise Barrier Legally Required?
- 7 Powerful Ways Industrial Curtain Walls Boost Employee Productivity
- Noise Enclosures vs. Traditional Soundproofing: Which Is Right for Your Facility?
- Steel Guard Safety Achieves SBA HUBZone Certification, Expanding Government Market Opportunities
- 5 Myths and 5 Truths about Smoke Curtains
- 7 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Setting Up Machine Guarding Fences
- Industrial Curtain Walls: 6 Reasons Why Manufacturing Facilities Must Have Them
Categories
- Accordion Fold Curtains
- Acoustic Baffles
- Agri-Shield Curtains
- Auto Body Shop Curtains
- Bio Plastics
- Draft & Smoke Curtains
- Industrial Divider Curtains
- Industrial Safety Products
- Insulated Curtain Walls
- Machine Guard Safety Fencing
- Mesh Curtain Screens
- News
- Outdoor Curtains
- PVC Strip Curtains
- Smoke & Draft Curtains
- Soundproof Noise Blocking Curtains
- Spray Paint Booth Curtains
- Tarps
- Thermal Curtains & Covers
- Uncategorized
- Warehouse Dividers
- Welding Blankets
- Welding Curtains
- Welding Screens